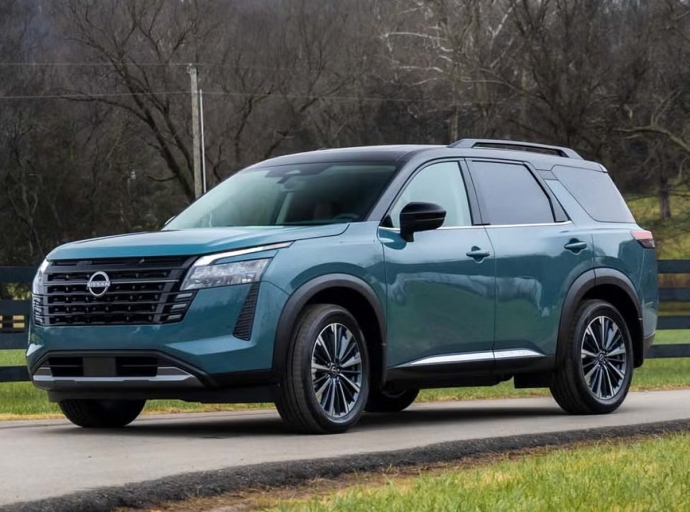
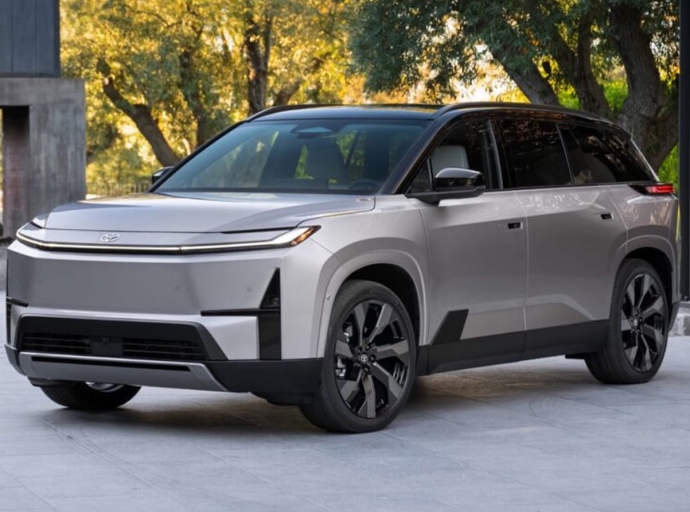
The arrival of new president Yvan Espinoza at the helm of Japanese automaker Nissan seems to have energized the company’s decision-makers. Several reports and rumors suggest that Nissan is in the process of revising its sales strategy.
Mechanics
Two New Nissan Pathfinder Models?
The arrival of new president Yvan Espinoza at the helm of Japanese automaker Nissan seems to have energized the company’s decision-makers. Several reports and rumors suggest that Nissan is in the process of revising its sales strategy.
...
All Stories
Éric Descarries
Éric Descarries

L'Automobile Magazine
News
Business Directory



 En
En  Fr
Fr 












