Collision
Carrosserie Denis Inc Strengthens Its Market Position by Earning Official Certified Collision Center Status
The Challenges of Repairing Electric Vehicles and Emerging Manufacturers

Adapting to an Electrifying Future
The automotive industry is undergoing a major transformation with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and their advanced technologies. For collision repair professionals, this revolution presents both significant opportunities and major challenges — especially when it comes to newer manufacturers such as Tesla and VinFast. Repairing an EV is far from a matter of simply applying traditional techniques; it requires understanding new systems, mastering innovative materials, and following strict safety protocols.
A Complex, High-Tech Architecture
Next-generation EVs are packed with advanced technology. In addition to their high-voltage batteries — the energy core of the vehicle — they integrate sophisticated electronic management systems, lightweight materials like aluminium and composites, and cutting-edge safety devices.
One of the major challenges for repair shops is learning how to work on these complex architectures without damaging critical components. For instance, removing or repairing parts located near the high-voltage battery requires an in-depth knowledge of disconnection and safety procedures. A single mistake could lead to electrocution or fire hazards.
Electric drivetrains also make body repair more difficult in certain areas. Many interior and exterior panels are located near high-voltage components such as power cables. A qualified technician must carry out the high-voltage disarming procedure.
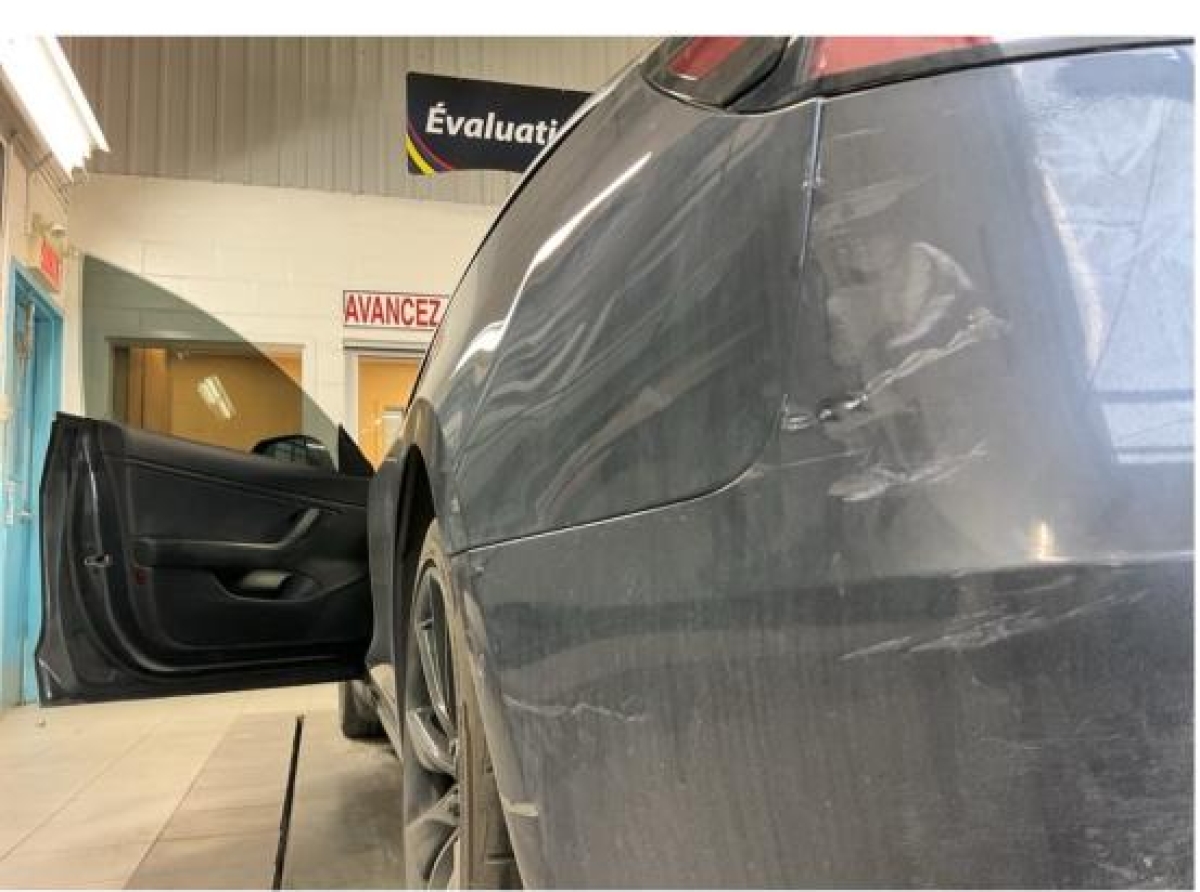
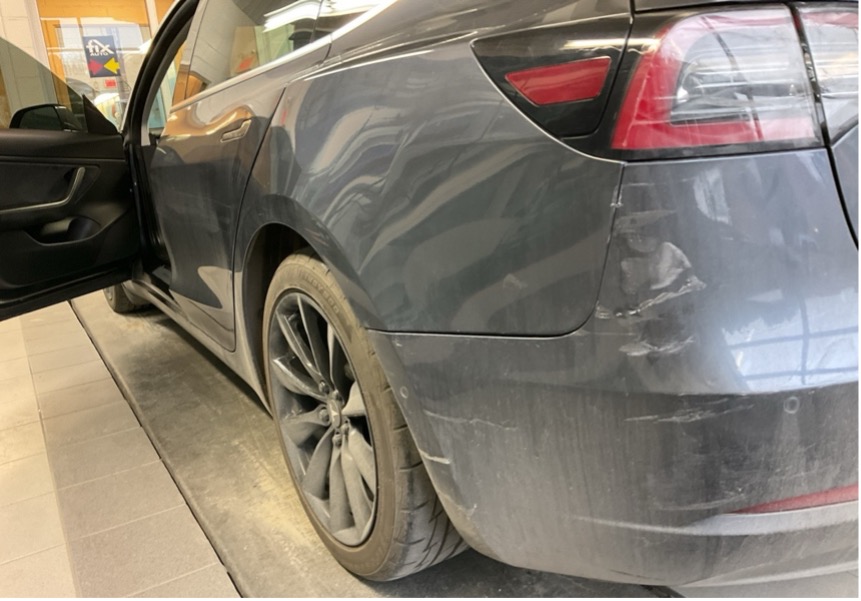
As shown in the adjacent image, a small dent on the rear left quarter panel required a complex repair because the charging cable ran behind it. When employees are properly trained and informed, these types of repairs become much more manageable and efficient.

Training: A Critical Foundation
Due to this complexity, training has become essential for collision repair professionals. The skills required to work on EVs go far beyond those needed for traditional gas-powered vehicles. It’s not just about mastering the basics of the trade — it means acquiring specific knowledge in:
- Electrical and electronic systems
- New materials used in EV frames and bodies
- Safety protocols, especially when working on high-voltage batteries
Automakers are increasingly partnering with training centres to offer certifications tailored to these needs, even for newer brands. These programs help repair technicians stay current with the latest innovations, while equipping them with the tools and information needed for efficient repairs. At DCF, we offer this kind of training, specifically designed for men and women working in the collision repair industry.
Next-Generation Materials
Electric vehicles commonly use lightweight materials such as aluminium, carbon fibre, or composite alloys to extend range. However, these materials present unique challenges for repair. Unlike standard steel, they require specific tools and methods to be handled or welded without compromising quality.
For example, straightening an aluminium panel demands great precision and the use of specialized welding tools. Additionally, some alloys cannot be repaired using conventional techniques and must be replaced — potentially increasing the customer’s bill. As shown in some examples, galvanic corrosion can occur between two different materials, leading to major issues during repairs. Newer vehicle manufacturers often have less experience with body design, particularly in Quebec’s climate, and this can lead to significant medium- and long-term problems.

Safety Constraints
Safety is a primary concern in EV repair, due to the presence of high-voltage battery systems. Before any work is done, the battery must be disconnected and checked for residual current. Failing to follow proper procedures can have serious consequences for both the vehicle and the technician.
Additionally, EV bodies are often equipped with sensors and radars for driver assistance systems (ADAS). These must be recalibrated after each repair to ensure proper operation. If not done correctly, the safety of both the driver and passengers may be compromised.

Les coûts et investissements
L’adaptation aux VÉ exige des investissements importants de la part des ateliers de carrosserie. Ces derniers doivent se doter d’équipements spécialisés, tels que :
Des outils d’isolation pour travailler sur les batteries haute tension ;
Des systèmes de diagnostic électroniques avancés ;
Des stations de calibration pour les capteurs ADAS.
Ces investissements, bien que coûteux, sont essentiels pour rester compétitifs sur ce marché en pleine expansion. De plus, ils permettent de répondre aux attentes croissantes des clients, qui recherchent des réparations rapides et de qualité.
Un avenir prometteur pour les carrossiers adaptatifs
Malgré ces défis, la transition vers les véhicules électriques offre des perspectives intéressantes pour les professionnels de la réparation automobile. Les ateliers capables de s'adapter aux nouvelles technologies bénéficieront d'un positionnement avantageux sur un marché en pleine croissance. En investissant dans la formation, les équipements et les certifications, les carrossiers peuvent non seulement répondre aux besoins actuels, mais aussi se préparer aux évolutions futures, comme l'arrivée des véhicules autonomes.
Conclusion
L'électrification de l'automobile marque une nouvelle page dans l'histoire de la carrosserie. Si les enjeux techniques, sécuritaires et financiers sont nombreux, les opportunités ne manquent pas pour les ateliers qui sauront relever ces défis. En s'engageant résolument dans cette transition, les carrossiers peuvent transformer ces obstacles en véritables leviers de croissance et d'innovation. Après tout, dans l'univers de la réparation, comme dans celui de la route, l'important est de savoir prendre le virage au bon moment.

L'Automobile Magazine
News
Business Directory



 En
En  Fr
Fr 


